
Laser is one
of the most important invention in the field of science. It changed
the traditional thinking about light. Lasers are useful in medical
and engineering fields - it is useful to people having dental problems
, cancer , thyroid problems or any other disease. Lasers are widely
used in engineering field .
We discuss this
topic under following headings
1. Introduction to laser
2. Quantum transitions
3. Population inversion
4. Pumping
5. Ruby lasers
6. He-ne lasers
7. Semiconductor lasers
8. Properties of lasers
9. Engg. application of lasers
1.
Introduction To Laser
Lasers are the
conventional source which have very high monochromaticity, intensity
and directionality. It fulfils the requirements of modern science
, technology about that source of light which is highly monochromatic
and have very high intensity. First successful laser was built by
T. H. Maiman in 1960 .
2.
Quantum Transitions
Transition of
an atom or molecule from one energy level to another is called the
quantum transitions. Usually three types of quantum transition.
(a) Absorption :- In this type of quantum
transition atom in lower energy state after absorption of energy
get excited
to higher energy state.
If atom in E1 energy state after absorption of energy hv get excited
to energy state E2 then,
E2 - E1 = hv (v is frequency nu)
* The number transitions at any instant depend on number of atoms
in state E1.
(b) Spontaneous
emission :- In this type atom in excited state drops down
to lower energy state with out using any external agency(force,energy).During
this there is emission of energy equal to nhv (E2 - E1).This is
a random and uncontrollable process.The no. of emissions depend
on the no. of atoms present in the energy level E2 (i.e.N2). This
transition occur only when N2>N1.
(c) Stimulated
emission :- In this there is drop down of atom from higher
energy to lower energy state with the help energy supplied In this
no. transitions depend on no. of atoms in higher energy state. This
process can be controlled and it is directional process. In this
transition no. of photons get doubled. This occurs only when N2>N1.
This type of transition is used in lasers.
3.
Population Inversion
From the above
processes, stimulated emission and spontaneous emission occur only
when N2>N1 . But in ordinary condition (normal temperature &
pressure) N2 cannot greater than N1.(it is possible only when temperature
is negative and negative temperature cannot be obtained).
* When population of higher energy state is higher than the lower
egergy state then that situation is called population inversion.
Population inversion can also be called as negative temperature
state. It can be achieved by pumping.
4.
Pumping
The process
of supplying energy to the medium in order to transfer it into the
state of population inversion is called pumping.
There are various methods of pumping, following are some of those
-
(a) Optical pumping:- Higher
population of upper energy level is achieved by supplying light
energy.This pumping can be used to any laser medium(solid,liquid,gaseous).
(b) Electrical
pumping :- In electrical pumping population inversion is
achieved by means of sufficiently intense discharge in the medium.
Electrical pumping can only be used with lasor meterial that can
conduct electricity without destroying laser action.
(c)
Chemical pumping :- When the population inversion is achieved
by suitable exothermic chimical reaction in the active material
is known as chemical pumping.
(d)
Heat pumping :- Population inversion is achived by means
of increaing the temperature.
On the basis
of no. of levels pumping is again classified, 1).Three level pumping,
2).Four level pumping.
The life-time of excited atom is less then 10 nano sec.However there
exists some states in which the life time is greater than 10 nano
sec.These states are known as metastable state.
5.
Ruby Lasers
In 1960 Miaman
built the first working laser.That was ruby laser. It is solid state
laser. Ruby is an aluminium oxide crystal, containing about 0.05%(by
weight)of chromium oxide.The chromium ions constitute the active
centers. Chromium ions give pink colour to ruby rod.The ruby rod
is cut and polished such that the end faces are optically flat and
exactly parallel to each other and are strictly perpendicular to
the axis of the rod. The faces are coated with a highly reflecting
material.Ruby rod is surrounded by a spiral flash tube.Chromium
ions are excited by absorption of photons from flash tube.The resulting
emission occurs in a releative broad spectral range centered about
696.3 nano meter.The beam is of red colour having wavelength 696.3
nano meter and a line width of about 0.0001 nano meter. It lastes
for about 7 meters.
6.
He-Ne Lasers
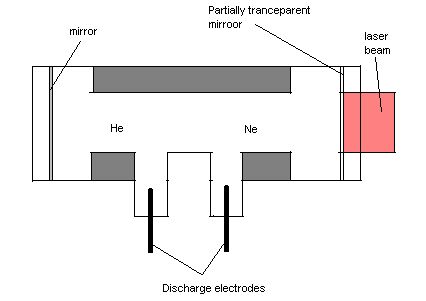 In
1960 Ali Javan and his co-workers at Bell Telephone laboratories
fabricated first helium-neon laser.In He-ne lasor the mixture of
helium neon is in the ratio 10:1 placed in long narrow discharged
tube. The pressure is kept at about 1mm of Hg. Pumping is accompanied
by electric discharge.Free electrons and ions are accelarated by
the applied electric field and excite the gaseous medium through
collisions.The dominant laser transitions correspond to 1152.3 nano
meter and 3391.2 nano meter in infrared region.
In
1960 Ali Javan and his co-workers at Bell Telephone laboratories
fabricated first helium-neon laser.In He-ne lasor the mixture of
helium neon is in the ratio 10:1 placed in long narrow discharged
tube. The pressure is kept at about 1mm of Hg. Pumping is accompanied
by electric discharge.Free electrons and ions are accelarated by
the applied electric field and excite the gaseous medium through
collisions.The dominant laser transitions correspond to 1152.3 nano
meter and 3391.2 nano meter in infrared region.
7.
Semiconductor Lasers
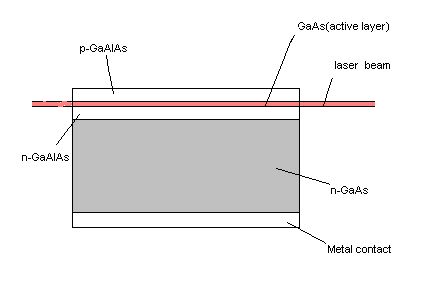 In
semiconductor laser a very highly doped pn junction in forword bais
is used to obtain laser action. When recombination of electrons
& holes takes place near junction energy is released in the
form of heat in case of Ge & Si semiconductor, but in case of
Gallium arsenide(GaAs) this energy is released in the form of light.
This property is used in semiconductor laser.
In
semiconductor laser a very highly doped pn junction in forword bais
is used to obtain laser action. When recombination of electrons
& holes takes place near junction energy is released in the
form of heat in case of Ge & Si semiconductor, but in case of
Gallium arsenide(GaAs) this energy is released in the form of light.
This property is used in semiconductor laser.
8.
Properties Of Lasers
Laser is differ
from light in many properties, following are some of those properties
(a) Monochromaticity
:- Laser light is much more monochromatic than any other light sources
(it is highly monochromatic)
(b) Lasers are
characterised by very high degree of coherence.
(c) Laser light
is emitted only in one direction not in all directions like other
light sources.
(d) Lasers have
very high intensity & are brighter than any other sources of
light.
9.
Engineering Application Of Lasers
Lasers have
many applications in the fields of medical & engineering; Following
are some of engineering applications,
(a) Laser can be used for drilling very soft as well as hard material.
(b) Laser can be ued for the cutting, it can act as knife.
(c) Laser can be used for welding work.