 |
 |
| Engineering
Mechanics |
By
- Suyog D. Chafale
|
Engineering mechanics
one of the interesting subject of first year B.E. This subject has
many practical applications and without this subject one cannot think
about working of machines ,force systems and vehicles etc. One can
say that this is the principal subject of mechanical engineering.
Syllabus for the first year B.E.student is not very varst as this
subject in itself is. But the whole syllabus cannot be discused through
this medium. I have tried to help with the subject by discussing the
experiments of E.M. as prescribed by the Nagpur University to help
you solve the discussion questions to be written in the journal.The
definations and diagrams will help to prepare this subject.
|
|
Experiment No : 1 |
Aim
:- Determination of law of machine using double purchase crab
|
Q.1) Discuss the importance of load vercus efficiency graph?
Ans:-The graph shows the relationship load and efficiency. The efficiency
can be easily found out for intermediate e values of load using graph.
The curve starts from origin and being a stright line upto certain
extent efficiency increases as load increases.
There after small increases in efficiency is observed when load increased.
Q.2) Discuss the
importance of load vercus ideal effort graph?
Ans:-The graph gives relation between load and and ideal effort.As
the graph is stright line effort increases with increases in load.
|
| Experiment No
: 2 |
Aim
:- Determination of law of machine using differential axle and wheel
|
Q.1) Discuss the importance of load versus effort graph?
Ans:-Ideal effot is effort required to lift a load neglecting the
machine friction. The graph shows relation between load and effort
and it can be expressed as
P = mW + C.
m - slope of line
W - load
C - y intercept of line
Q.2) Discuss the
causes of possible errors?
Ans:- a)Experimental error. b)Manual error. c)Error due to friction.
Q.3) Discuss the
fritional loss in machine?
Ans:-For an ideal machine Pi=W/(V.R.). At W=0 the effort=C and will
lift up the load, for an actual motion of machine a effort Pf is required
to overcome the friction at load W and is given by P - Pi which is
Pf = mW + C - W/(V.R.)
If increses with load.
Q.4) How should
the effort vary with the load for an ideal machine? How does the plat
after due to friction?
Ans:-For an ideal machine erergy supplied equals to useful warkdone
suppose load lifting by idealmachine is ' W '.The applied effort is
' P 'and velocityratio is ' V '.When load moves a unit distance then
distance coverded by effort is equal to ' U ' .
Therefore,energy supplied is equal to ' PV '.
Useful work done is equal to ' w '.
w = P .V
Therefore , W / P = V =mA
Hence for ideal machine effort vary directly with load.
Q.5) Of the various
lifting machines known to you how would you decide which are to choose
for a particular situation?For example which lifting machine is best
suited in your opinion for the following jobs.
a)Lifting a drum of water from a well.
Ans:-Pulley.
b)Lifting a heavy
consigment from ship.
Ans:-Crain.
c)Lifting the
body of a truck for changing wheels.
Ans:-Jack.
|
| Experiment
No : 3 |
Aim:-Determination
of coefficient of static friction by inclined plane setup
|
Q.1) What will be the value coefficient of static friction if (a)both
materials are glass and (b)if both materials are wood ?
Ans:- If both the materials are glass the coefficient of friction
will be less,and if both materials are wood then coefficient of friction
is more.
Q.2) Define angle
of repose?
Ans:-It is the max. inclination of the plane at which a body can remain
in equillibrium over the plane entirely by the assistance of friction
is called angle of repose.
Q.3) Suppose a
block is placed on the indine and there is no pulley and string etc.
Can' t we find the coefficient of static friction by creating condition
of downward impending motion ? By increasing the inclination 0 ; by
adding more weight on the block ? Can we ? How would it compare with
our method ?
Ans:- We can find coefficient ob static friction by creading a downward
impending motion .This can be done slowly increasing the angle of
inclination till the body just starts to move.At this stage angle
of inclition will be equal to angle of friction . This practically
will not possible be possible because body will mov very fast and
motion will take place with in fraction of second and observation
can ' t be taken.
Q.4) The assumption
made in analysis of observation and frictional pulley inextensibility
of string .How correction of masses and angle measured .How far are
the assumptions justified and what are possible sources of error ?
Ans:- The error may be due to stright friction present in pully .May
be mass measurment may not be acurate .Error in measurment of angle
friction as angke is cal culated by geometric method.
|
| Experiment
No : 4 |
Aim:-Determination
of coefficient of friction using coil frction setup
|
Q.1) Differentiate between sliding friction and coil friction?
Ans:- Sliding friction
a) It is a friction experemied by a body when it slides over other
body.
b) It is a type of dynamic friction.
c) It is comparatively more.
Q.2) What is importance and use of coil friction ?
Ans:-We can determine the tension experiecned by body when friction
exits.We can determine the friction force experienced, we can also
find minimum force required to keep it in equillibrium.
Q.3) What is the
importance angle of lap and its practical application ?
Ans:- Angle of lap is useful to determine tension on both sides of
string/rope.Greater the angle of lap lesser the tension at free end
of ropes.
|
| Experiment No
: 5 |
Aim:-
Determination of reaction using coplaner parallel force system
|
Q.1 )What are the reasons for the deviation in therotical value and
expt. value?
Ans:-
a)The wts. used in expt may vary from actual value.
b)The least count of dial spring is not sufficiently small to read
actual reading.
c)Human error.
d)The lengths are not measured correctly.
Q.2) Can a load
postion be determined to obtained given reaction?
Ans:-Yes when reactionon the beam is given then by taking moment of
those reactions and unknow values of load about a point ,and taking
summesion along x and y direction. Then solving the equation simultaneously.
Q.3) Sketch various
types of beams.
Ans:- 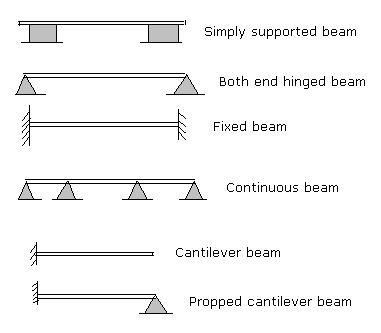
Q.4) Why generaliy beam is supported by one hinge and one roller supports
?
Ans:- When external forces are attached or applied to a body which
is hinged from both end then the body may bend or break due to deforming
force devepol due to external force ,and if both the supports are
roller supports then is not fixed and it can move in any direction
.
Hence one support is hing and other is roller support.
Q.5) Sketch various
beam sections.
Ans:- 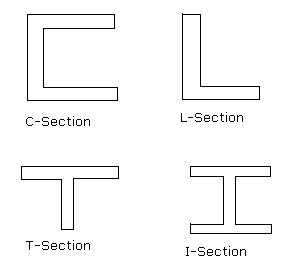
|
| Experiment No
: 6 |
Aim:-Determination
of forces using coplaner concurrent force system
|
Q.1) What will be the effect on the forces if the tie is attached
in such a fashion that point C is lower than point B ?
Ans:-If point c is lower than point B then than tension in string
will reduce greatly and due to that jib will be compressed to such
an extent that the forces in jib gecreases and set up becomes unstable
.
Q.2) What is jib
crane ?
Ans:-Jib crane setup consists of compressive member (jib) and tension
member which is connected by a load.
The jib crane operates a principal of coplanner concurrent force system.
Thus for a jib crane to be in eqillibrium ,total forces should be
balanced.
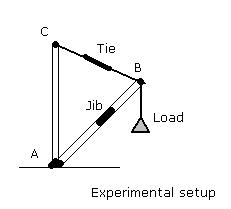
Q.3) What are
the reasons for the error ?
Ans:-
a)Friction in jib
b)Error in measurment of lengths
c)Variation in value of wts.
d)Human error.
|
| Experiment No
: 7 |
Aim:-Determination
of M.I. using fly wheel
|
Q.1) Define "mass
moment of inertia"
Ans:- Mass moment of inertia :- The moment of inertia about a given
axis of rotation for a rigid body is defined as sum of product of
mass of each particle and square of perpendicular distance from the
axis of rotation. Moment of inertia plays important role in circular
motion as that of mass in linear motion . Hence physical significance
of M.I. is same as of mass. Hence it is called mass moment of inertia.
Q.2) Differentiate
between inertia and moment of inertia.
Ans:- a) Inertia is the tendency of bodyto maintain its state of rest
or of uniform motion while moment of inertia is the mass equivalent
in the rotational motion.
b) Inertia is the tendency of a body while moment of inertia is a
property of body which it gains in rotational motion.
c)Inertia is applicable to translational motion where as moment of
inertia is applicable to angular motion.
Q.3) Diffenentiate
between fly-wheel and solid disk wheel.
Ans:- a) Moment of inertia of fly-wheel is 5/4 times that of uniform
disk.
b) Mass is uniformly distributed in case of disk while it is concentrated
at the circumference of fly-wheel.
Q.4) In the expt.
of determination moment of inertia what is the importance of accuracy
in measurment of time ?
Ans:- Time measured is used to calculate angular velocity and linear
velocity. If time is measred is accurate then angular velocity can
becalculated accurately. Following are the factors causes error in
measurment of time
a) Human error in starting and stopping the clock.
b) Least count of clock may not be sufficiently small.
Q.5) Explain why
a flywheel should have a large M.I.?
Ans:As contribution of mass is away from the axis of rotation so flywheel
should be have a large M.I..
Q.6) Can you suggest
some alternative method for determing moment of inertia of a body
about a given axis?
Ans:It can be found by first calculating centriod of area then find
M.I.about centridal axis and now with the help of parallel and perpendicular
axis principle transfer M.I. to required axis.
|
 |